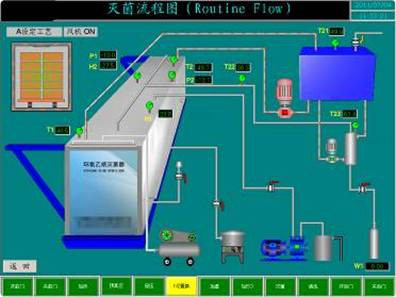
(2) Sterilization refers to killing or removing all microorganisms (including spores) on the transmission medium to achieve sterility. Sterilized items are called "sterile items".
Principles of disinfection and sterilization
(1) Identify the main objects of disinfection. Specific analysis should be made on the ways of causing pollution, the types of media and pathogenic microorganisms involved, and disinfectants should be used in a targeted manner.
(2) Adopt appropriate disinfection methods According to the disinfection objects, select simple, effective, non-damaging disinfection methods, abundant sources, and moderate prices.
(3) Controlling the factors that affect the effect of disinfection Many factors affect the effect of disinfectants, and the sensitivity of various disinfectants to these factors varies greatly.
Types of microorganisms Different types of pathogenic microorganisms have different resistance to disinfectants. Therefore, they must be treated differently when disinfecting.
(1) Bacterial propagules are easily destroyed by disinfectants. Generally, Gram-positive bacteria are more sensitive to disinfectants, while Gram-negative bacilli often have stronger resistance. The propagule is sensitive to heat, and the main disinfection method is heat disinfection.
(2) Bacterial spores The spores have strong resistance to disinfection factors, and the reliable methods to kill bacterial spores are heat sterilization, ionizing radiation and fumigation. In chemical disinfectants, hydrogen peroxide can kill spores.
Methods of disinfection and sterilization
(1) Physical disinfection and sterilization
The use of physical factors to kill microorganisms. Including thermal disinfection, radiation disinfection, air purification, ultrasonic disinfection and microwave disinfection.
1. Heat disinfection and sterilization High temperature can denature or coagulate microbial proteins and enzymes (structural changes lead to loss of function), and the metabolism will be hindered and die, so as to achieve the purpose of disinfection and sterilization. In disinfection, heat can be divided into two categories: damp heat and dry heat.
Damp heat sterilization
Moist heat sterilization is conducted by air and water vapor, with fast heat transfer and strong penetration. Moist heat sterilization requires lower temperature and shorter time than dry heat sterilization.
(1) Boiling method Boil water to 100, keep it for 5-10 minutes to kill the propagules, keep it for 1-3 hours to kill the spores.
(2) High Pressure Steam Sterilization Method Before the high pressure steam sterilizer is boiled, the items are rinsed and cleaned. Open the shaft section or cover and immerse all of them in water.
UV disinfection
When the room temperature is 20~25, the intensity of 253.7nm ultraviolet radiation at the vertical position 1.0m below the 220V 30W ultraviolet lamp should be 70W/cm2, and should be replaced when it is lower than this value. The appropriate number of ultraviolet lamps should ensure that the average per cubic meter should be more than one. At 1.5W. During ultraviolet disinfection, the sterile room should be kept clean and dry. Personnel can enter work only after turning off the UV lamp for at least 30 minutes.
(2) Disinfection of chemical reagents
(1) Formaldehyde disinfection:
The formaldehyde mentioned here is a 40% formaldehyde solution, that is, formalin. The general package says 37%. Disadvantages: Formaldehyde is too harmful to the human body, and this method is generally not recommended.
(2) Hydrogen peroxide: Both hydrogen peroxide and colloidal silver ions can penetrate and destroy the cell wall and cell membrane of microorganisms, enter the cell interior to necrosis key functional components (such as DNA and enzymes), thereby Causes cell death.
Based on the above characteristics, the imported sporicide of the Norfo brand as a new type of disinfection product is unmatched by other disinfectants. It can be used as an alternative disinfectant for disinfection of clean areas or as a substitute for Prostaglandin, ensuring that the environmental microorganisms in the clean area meet the requirements of GMP. The quality of the products produced benefits the enterprise.